SwiftUI 並行性Concurrency的使用 - OperationQueue方式
xcode 13.4.1, swift 5.5, iOS 15.4
2022-09-07
由於現在的電話使用的CPU都是多核的,所以更好的利用多核的優勢,目前很多App都是使用並行性來最大程度的利用多核的計算能力,這次就講講如何使用Swift提供一種並行性方式OperationQueue。
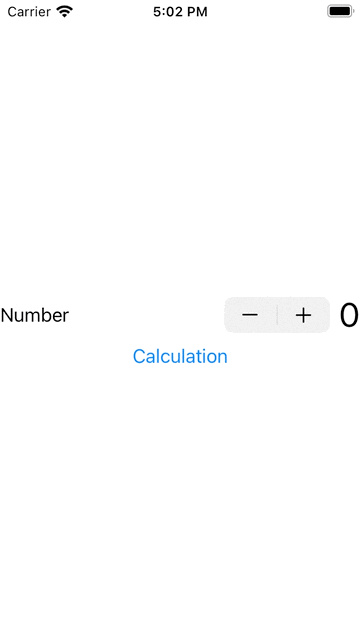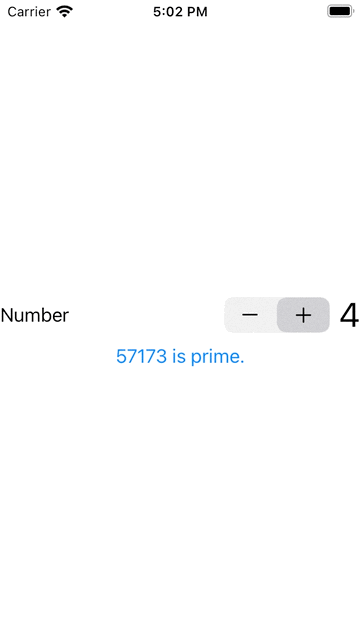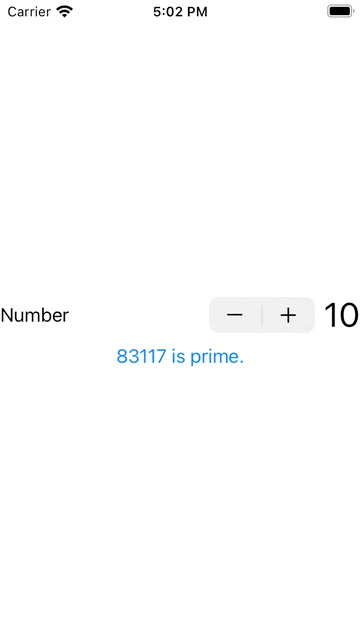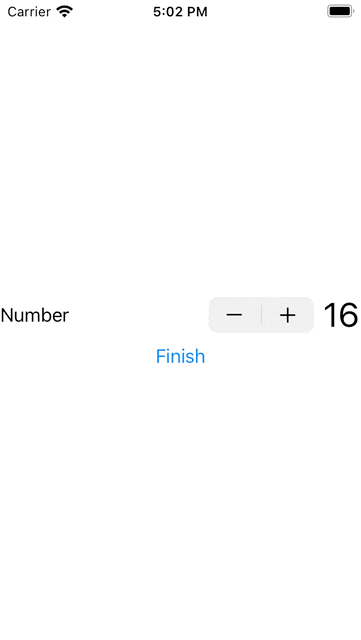
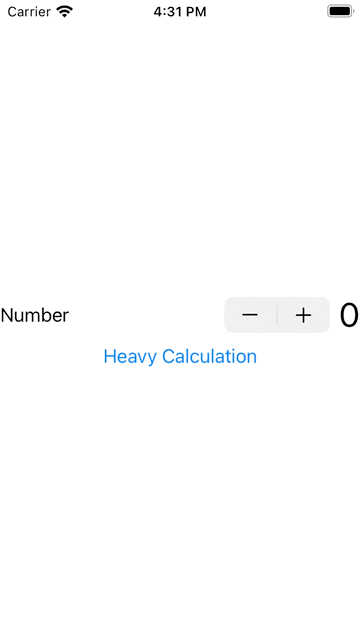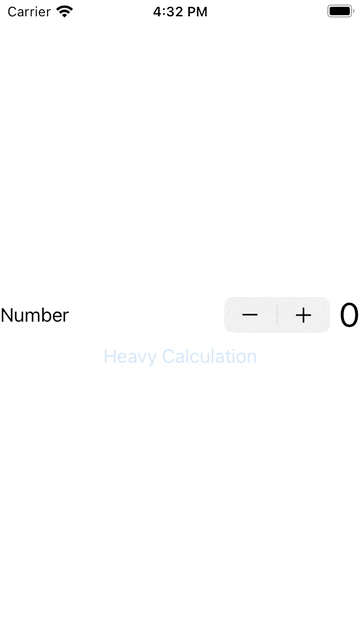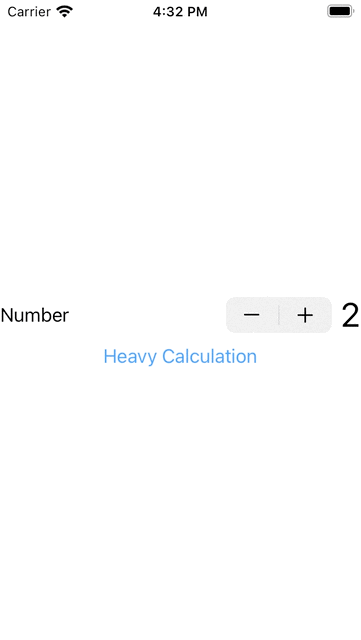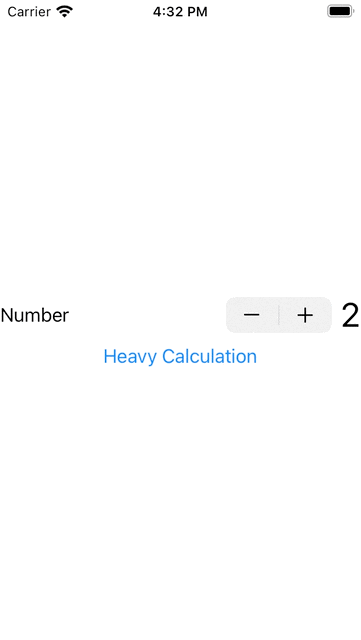
1. 下面我演示一個要做很長時間的動作,會影響其他元作,如下按下Stepper是沒有反應,要等到做完計算後才會有反應:
import SwiftUI
struct ConcurrencyExample: View {
@State private var num : Int = 0
var body: some View {
VStack {
HStack {
Stepper("Number") {
num = num + 1
} onDecrement: {
num = num - 1
}
Text("\(num)").font(.largeTitle)
}
Button {
heavyCalculation()
} label: {
Text("Heavy Calculation")
}
}
}
func heavyCalculation() {
for i in 0...100000 {
if isPrime(i) {
print("\(i) is prime.")
}
}
}
func isPrime(_ n : Int ) -> Bool {
if n<=1 {
return false
}
if n<=3 {
return true
}
var i = 2
var flag = false
while (!flag && i<n) {
flag = (n % i == 0)
i = i + 1
}
return !flag
}
}
2. 為了解決這種問題,我們可以使用OperationQueue來使用多核的優勢。我們創建一個繼承Operation的class,並在func main()寫上需要很長時間計算或運行的程式,然後把這種class的object加入OperationQueue中就可以使用多核的優勢了。
import SwiftUI
struct ConcurrencyExample: View {
@State private var num : Int = 0
var body: some View {
VStack {
HStack {
Stepper("Number") {
num = num + 1
} onDecrement: {
num = num - 1
}
Text("\(num)").font(.largeTitle)
}
Button {
heavyCalculation()
} label: {
Text("Heavy Calculation")
}
}
}
func heavyCalculation() {
let queue = OperationQueue()
let heavyCalculationOperation = HeavyCalculationOperation()
queue.addOperation(heavyCalculationOperation)
}
}
class HeavyCalculationOperation : Operation {
override func main() {
heavyCalculation()
}
func heavyCalculation() {
for i in 0...100000 {
if isPrime(i) {
print("\(i) is prime.")
}
}
}
func isPrime(_ n : Int ) -> Bool {
if n<=1 {
return false
}
if n<=3 {
return true
}
var i = 2
var flag = false
while (!flag && i<n) {
flag = (n % i == 0)
i = i + 1
}
return !flag
}
}
3. 以上不太明顯,我們可以在計算過程之中改變Button的顯示文字,來更明顯的展示計算的過程,並在計 算過程中,其他元件不受影響。
import SwiftUI
struct ConcurrencyExample: View {
@State private var num : Int = 0
@State var calculateState : String = "Calculation"
var body: some View {
VStack {
HStack {
Stepper("Number") {
num = num + 1
} onDecrement: {
num = num - 1
}
Text("\(num)").font(.largeTitle)
}
Button {
heavyCalculation()
} label: {
Text(calculateState)
}
}
}
func setCalculateState(_ calculateState : String) {
self.calculateState = calculateState
}
func heavyCalculation() {
let queue = OperationQueue()
let heavyCalculationOperation = HeavyCalculationOperation(concurrencyExample: self)
queue.addOperation(heavyCalculationOperation)
}
}
class HeavyCalculationOperation : Operation {
let concurrencyExample : ConcurrencyExample
init(concurrencyExample : ConcurrencyExample) {
self.concurrencyExample = concurrencyExample
}
override func main() {
self.concurrencyExample.setCalculateState("Calculating ... ...")
heavyCalculation()
self.concurrencyExample.setCalculateState("Finish")
}
func heavyCalculation() {
for i in 0...100000 {
if isPrime(i) {
print("\(i) is prime.")
self.concurrencyExample.setCalculateState("\(i) is prime.")
}
}
}
func isPrime(_ n : Int ) -> Bool {
if n<=1 {
return false
}
if n<=3 {
return true
}
var i = 2
var flag = false
while (!flag && i<n) {
flag = (n % i == 0)
i = i + 1
}
return !flag
}
}